
Alternative investments (or Alternatives) are often discussed in the financial world but in our experience most investors do not have a clear idea of what alternative investments are or the role they play in a diversified portfolio. In this paper, we attempt to answer these questions. In addition, we discuss our firm’s philosophy and approach to incorporating Alternative investments in client portfolios.
What is an Alternative Investment?
In general terms, Alternatives are investments other than stocks, bonds and cash. Whereas stocks, bonds and cash are typically classified as traditional investments, we can think of Alternatives as non-traditional investments1. Alternatives can also be thought of as an asset class that is distinct from the traditional asset classes of stocks, bonds and cash.
Beyond these broad definitions, one of the main characteristics of Alternative investments is their relatively low correlation with traditional asset classes. By correlation we mean how investments perform relative to each other during different periods of time and across different phases of the market cycle. As we will discuss in more detail, lower correlation among investments is desirable because this reduces the overall risk or volatility of a portfolio.
There are different types of investments within the Alternatives universe. The most common are: real assets (including real estate, infrastructure and commodities), hedge funds and private equity. Table 1 below provides an overview of each of these types of investments.
Most Alternatives are characterized by lower liquidity compared to traditional asset class investments. This is particularly true for hedge funds and private equity. In these types of investments, investors are often required to lock- up their money for extended periods of time (up to 5 or more years in the case of many private equity structures). Within the real asset space, liquidity tends to vary significantly between different types of investments. In the case of real estate, there are highly liquid investments such as public market real estate investment trusts (REITs), which trade everyday in the markets much like stocks. Conversely, there are private real estate investments that provide limited liquidity.
Historically, certain Alternative investments were largely reserved for institutional investors and accredited private investors, that is, investors with a minimum level of income and assets. In recent years, however, the market has seen the emergence of liquid alternatives, which are mutual funds that employ Alternative investment strategies. In particular, numerous mutual funds that offer hedge fund strategies are now available in the marketplace. Over time, liquid alternatives could expand the usage of Alternatives among retail investors. While the fees of liquid alternative investment vehicles tend to be noticeably higher than those of traditional stock and bond investments, they are generally lower than the fees that hedge funds and private equity firms typically charge their investors2.
What role do Alternative Investments play in a Diversified Portfolio?
In our view, Alternative investments play a valuable role in a diversified portfolio as they offer investors numerous benefits. These include: 1) improved diversification as a result of low correlations with traditional asset classes, 2) access to a wider menu of investment opportunities3 and 3) the potential to increase the aggregate yield of a portfolio.
Diversification is one of the most powerful concepts in investing. It has even been referred to as the “only free lunch in finance” because through diversification, investors are able to significantly lower risk without necessarily sacrificing returns4. The key to reducing risk in a portfolio context is to own investments that have low correlations with one another, meaning that the investments will perform differently from each other in different market environments. A classic example of this is the way that US government bonds tend to rise in price while stocks fall in price during market sell-offs. In a portfolio consisting of both stocks and US government bonds, the decline in value of stocks is partially offset by the rise in price of US government bonds thus reducing the overall risk or volatility of the portfolio. The low correlation between stocks and US government bonds is what makes this possible. Combining different types of investments to maximize the return vs risk profile of a portfolio is both the art and science of the portfolio construction process.
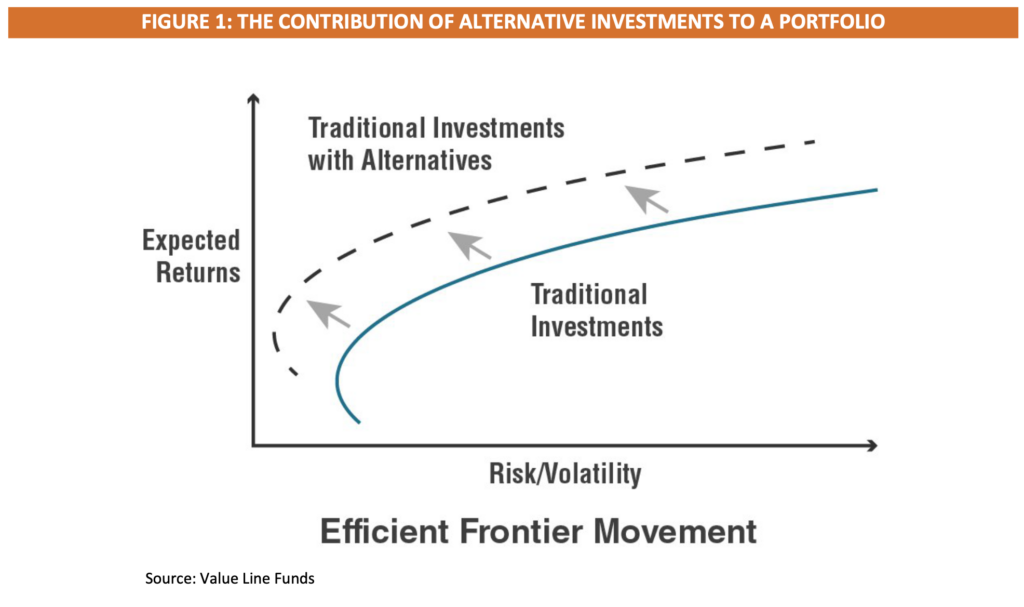
While the volatility dampening effect of US government bonds is perhaps the gold standard in terms of correlations, other types of investments can also improve the return vs risk profile of portfolios. In particular, Alternative investments tend to have low correlations with traditional asset classes. As a result, they are a valuable potential addition to the investment mix of a portfolio. Figure 1 below highlights how Alternatives can make portfolios more efficient by enhancing return and/or minimizing risk.
Beyond diversification, another benefit of Alternatives is that they expand the investment opportunity set, thus making more investment choices available to investors. This can be very valuable as the most attractive investment opportunities may be found outside of the traditional asset classes at certain points in time during a market cycle.
Lastly, another benefit of Alternative investments is that they have the potential of enhancing the yield of a portfolio. This is because certain segments of the Alternatives market, such as real estate, tend to provide investors with significant cash distributions (i.e. high yields). Today, for example, the average yields in the US real estate sector are noticeably higher than those in both the US stock and bond markets5. Therefore, a meaningful allocation to real estate will currently tend to increase the overall income generation of a portfolio.
Our Philosophy and Approach to Alternative Investments
While not all firms in our industry invest in Alternatives, in our view a strategic allocation to this asset class makes sense given its numerous potential benefits. Overall, we believe that Alternative investments enhance the quality of investor portfolios.
While we see value in adding Alternatives to the investment mix, we nevertheless believe that the traditional asset classes should form the bulk of investor portfolios. In our view, Alternatives are best utilized as a complement to, rather than as a substitute for, stocks and bonds. In our firm’s client portfolios, an allocation of 10% to Alternative investments is common today.
While we believe the investment case for Alternatives is compelling, it is important to acknowledge that there are complications to effectively implementing an investment strategy in this area. Most notably, the costs of investing in hedge funds and private equity strategies, either directly or through liquid alternatives, remain quite high. In addition, the performance of most hedge fund and private equity strategies has not been strong enough in recent years in our view to justify their high costs. Therefore, while we periodically evaluate investments in these areas, costs have effectively kept us away.
Instead, we have largely focused on real assets as the core part of our Alternatives investment strategy. In our view, real assets provide most of the benefits of Alternative investments (correlation benefits, expansion of the investment opportunity set, the potential for attractive yields, etc.) at a very reasonable cost. In addition, in most segments of the real assets space, it is possible to invest globally. This global reach adds an additional layer of diversification to client portfolios. For all of these reasons, our Alternative investments today are concentrated in the real assets area, particularly in real estate and infrastructure.
In Conclusion
Alternatives are investments other than stocks, bonds and cash. These non-traditional investments offer several potential benefits to investors, including: 1) improved diversification, 2) access to a wider menu of investment opportunities and 3) the potential to increase the yield of a portfolio. In our view, a strategic asset allocation to Alternative investments enhances the quality of investor portfolios. Within the Alternatives universe, we have a clear preference for real assets. We believe that these types of investments provide most of the benefits of Alternatives with the additional advantage that they can be accessed at reasonable costs.
ENDNOTES
1 https://www.blackrock.com/us/individual/education/what-are-alternative-investments.
2 The most common fee structure in the hedge fund and private equity world is 2% of annual assets under management plus 20% of annual profits.
3 Baird Private Wealth Management.
4 This quote is usually attributed to professor Harry Markowitz who is the founder of the economics school of thought known as Modern Portfolio Theory(MPT). Professor Markowitz was awarded the Nobel Prize for his work in this area.
5 The average yield of the US real estate sector is currently in the neighborhood of 3%. In contrast, the average yield of the US stock market is just under 2% while the average yield of the US aggregate bond market is in the range of 2.5%.
Investment Policy Statement
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Baird Private Wealth Management. “The Role of Alternative Investments in a Diversified Investment Portfolio.” April 2013.
CLS Investments. “The Investment Case for Real Assets.” January 23, 2018.
https://www.blackrock.com/us/individual/education/what-are-alternative-investments
SEC Office of Investor Education and Advocacy. “Investor Bulletin Hedge Funds.” SEC Pub. No. 139 (2/13). Value Line Funds. “Alternatives Investments: Incorporating a Turnkey Solution.” December 12, 2016. Voya Investment Management. “An Overview of Private Equity Investing.” October 2017.

